Organizations & Institutions
World Health Organization (WHO)
WHO was established on April 7, 1948, with the aim of bringing all people to the highest possible level of health. The WHO has many responsibilities, primarily setting norms and standards related to public health and ensuring their implementation.
The organization’s founding anniversary is celebrated as World Health Day.
Global Standards 1 (GS1)
GS1 is a non-profit organization that develops and maintains global standards for business communication. It has offices in over 100 countries and more than one million members.
GS1 standards are designed to improve the efficiency and traceability of supply chains. They define products, locations, assets, and more, creating a business language for sharing critical information.
The most well-known GS1 standard is the barcode—printed on products, electronically scannable, and containing unique data for each item.
Definitions
Rational Use of Medicines
Rational use of medicines means using the right drug, in the correct dose and at the right time, as prescribed by a physician. A drug is considered appropriate when it is effective for the user and meets acceptable standards of quality and safety. Rational use of medicines also involves the prescription, marketing, and use of approved medicines—authorized for safety, quality, and efficacy—according to national regulations and practices, by qualified professionals.
Pharmacovigilance (PV)
Pharmacovigilance refers to the scientific activities aimed at detecting, identifying, evaluating, and preventing adverse effects and potential problems related to human medicinal products.
Original and Generic Medicines
Original medicines are patented drugs based on molecules proven through extensive research and clinical trials to have a positive effect on specific diseases.
Generic medicines are lower-cost alternatives derived from original medicines, containing the same active substance in the same amount. They must be proven to be bioequivalent to the original.
Stakeholders
Stakeholders are individuals, institutions, or organizations that can influence or be affected by the system’s activities, policies, and outcomes. In the Pharmaceutical Track & Trace System, stakeholders include manufacturers, importers, exporters, pharmacy warehouses, pharmacies, consumption centers (hospitals, polyclinics, family health centers etc.), and consumers.
Consumables
In consumption centers like hospitals and family health centers, drugs are dispensed individually. For example, capsules used for an injection are taken from a box, and the remaining ones are used for other patients. Such single-use items are classified as medical consumables.
Recall Process
A recall is the removal of a defective or potentially defective drug from the market by the responsible company, based on defined levels. The urgency and severity of the issue determine the recall level.
Hospital Information Management System (HIMS)
HIMS tracks all hospital operations—tests, lab/pathology results, operating room procedures, pharmacy processes, HR, etc.—by integrating various specialized software into a unified system.
Global Location Number (GLN)
This is a unique number assigned by GS1 to identify any location within the supply chain. It is used to identify physical sites and legal entities.
Serial Shipping Container Code (SSCC)
Companies use SSCC to identify logistic units (any combination of trade items) prepared for storage or transport. This code is essential for traceability, as each SSCC uniquely identifies a shipment and its contents. SSCC data can be shared via EDI or EPCIS to link products to transport events.
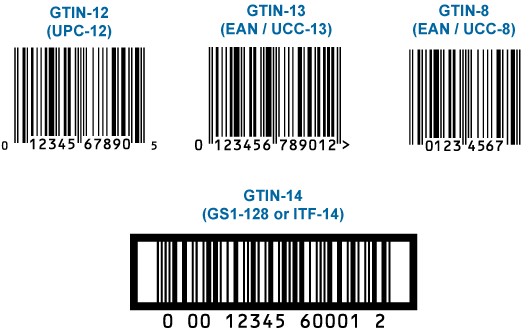
Global Trade Item Number (GTIN)
GTIN is used for every level of packaging that can be bought and stored. This number enables product identification for selling, buying, and warehousing.
GTINs work as keys in ADC systems to access product info. GTINs can be 8, 12, 13, or 14 digits. 12 digits are used in North America while 8 and 13 digits are in other regions. In Turkey, 13-digit combines company prefix and product number. On the other hand, 14 digits are for packaging level differentiation per GS1 standards.
Batch Number
This number is a unique ID to distinguish one production batch from others.
Serial Number (SN)
This number is a unique identifier for each individual product unit.
Expiration Date
This date indicates the last safe usage date for a product, in YYMMDD format (6 characters).
2D Data Matrix
It is a 2D barcode of black-and-white cells encoding numeric or text data. Its data capacity depends on matrix size. It is used on medicine boxes to speed up tracking via barcode scanners. It encodes GTIN, serial number, expiration date, and batch number. 2D Data Matrix is core to the Pharmaceutical Track and Trace System.

Extensible Markup Language (XML)
XML is a markup language for standardizing data exchange between systems. It is used for database migration, financial transactions, file systems, and scientific data storage.
